What Causes Women’s Hair Loss?
Women's hair loss can be caused by various factors, and it often involves a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental influences. Here are some common causes of hair loss in women:
Genetics (Hereditary Hair Loss):
Female pattern hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, is a genetic condition that can lead to gradual thinning of the hair. It tends to run in families and is influenced by the presence of specific genes.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in women's hair loss. This can occur during various life stages, including puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also cause hormonal imbalances and contribute to hair loss.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions and illnesses can lead to hair loss. These include thyroid disorders (hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism), autoimmune diseases (such as alopecia areata), and chronic illnesses.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Inadequate nutrition, especially deficiencies in iron, zinc, vitamin D, and B vitamins, can impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
Physical or Emotional Stress:
Intense physical or emotional stress, such as surgery, illness, trauma, or significant life changes, can trigger a condition known as telogen effluvium, causing temporary hair shedding.
Certain Medications:
Some medications, including certain types of birth control pills, anticoagulants, and medications for blood pressure, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Traction Alopecia:
Excessive pulling or tension on the hair due to tight hairstyles, braids, or hair extensions can lead to a type of hair loss called traction alopecia.
Chemical Hair Treatments:
Overuse of chemical treatments, such as frequent coloring, perming, or straightening, can damage the hair shaft and contribute to hair loss.
Aging:
Aging is a natural factor that can affect hair thickness and density. As women age, hair follicles may gradually shrink and produce finer hair.
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to environmental pollutants, harsh climates, or excessive sun exposure without protection can impact hair health.
Women experiencing hair loss have various options to potentially regrow hair or slow down further loss. Here are some strategies that women can consider:
Topical Minoxidil:
Topical minoxidil is an FDA-approved over-the-counter treatment for female pattern hair loss. It is applied directly to the scalp and may help stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss.
Prescription Medications:
Some prescription medications, such as spironolactone or finasteride, may be recommended by a healthcare professional to address hormonal factors contributing to hair loss. However, finasteride is usually not prescribed to women of childbearing age due to potential risks during pregnancy.
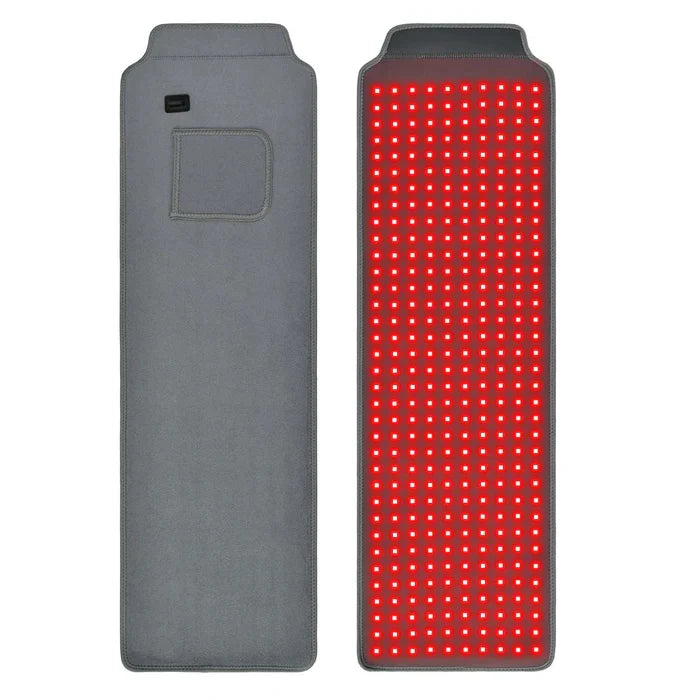
Red Light Therapy:
Red light therapy devices, such as red light helmets, or caps, use red or near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles. Some Researchs find these devices helpful in promoting hair growth.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient's blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and then injecting it into the scalp. PRP contains growth factors that may stimulate hair follicles.
Hormone Therapy:
For women with hormonal imbalances contributing to hair loss, hormone therapy may be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. This is especially relevant for conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Nutritional Supplements:
Ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients, including iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamins, can support overall hair health. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
Lifestyle Changes:
Managing stress through practices like meditation or yoga, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding excessive heat styling or harsh chemicals can positively impact hair health.
Scalp Massage:
Regular scalp massages can improve blood circulation to the hair follicles, promoting a healthy environment for hair growth.
Avoiding Tight Hairstyles:
Avoid hairstyles that cause tension on the hair, such as tight ponytails or braids, to prevent traction alopecia.
Consultation with a Dermatologist:
If experiencing significant hair loss, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They can provide a thorough evaluation, diagnose the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatments.
It's crucial for women to seek professional guidance before starting any hair regrowth treatment. The effectiveness of these approaches can vary, and an accurate diagnosis is essential to tailor the treatment plan to the specific cause of hair loss.