Androgens:
Androgens are male sex hormones that include testosterone and its derivative, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Both men and women produce these hormones, but they are present in higher levels in men.
Effect on Hair Loss: Elevated levels of DHT can shrink hair follicles and make them more susceptible to falling out. This process, known as miniaturization, can lead to a condition called androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness.
Estrogens:
Estrogens are female sex hormones. While they are present in both men and women, they are more predominant in women.
Effect on Hair Loss: Estrogens have a protective effect on hair, promoting hair growth. Changes in estrogen levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can influence hair growth patterns. Some women may experience temporary hair loss postpartum or during menopause.
Progesterone:
Progesterone is another female sex hormone that plays a role in regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining pregnancy.
Effect on Hair Loss: Changes in progesterone levels, such as those during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can affect hair growth. A decrease in progesterone levels may contribute to hair shedding.
Thyroid Hormones:
Thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), regulate the body's metabolism and energy production.
Effect on Hair Loss: Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can lead to hair loss. Hypothyroidism, in particular, is associated with hair thinning and brittleness.
Cortisol (Stress Hormone):
Cortisol is a hormone released in response to stress and helps the body respond to stressful situations.
Effect on Hair Loss: Prolonged stress and elevated cortisol levels can contribute to a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, where a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase, leading to increased shedding.
Factors to Consider:
Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in how hormones affect hair loss. If there is a family history of androgenetic alopecia, individuals may be more predisposed to hormone-related hair loss.
Age: Hormonal changes associated with aging can influence hair growth patterns.
If you are experiencing significant hair loss or have concerns about hormonal influences on your hair, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or endocrinologist. They can perform tests to assess hormone levels and help determine the most appropriate course of action.
How to Grow Healthier Hair
Growing healthier hair involves a combination of proper hair care, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle. Here are some tips to help you grow healthier hair:
Balanced Diet:
Protein Intake: Hair is primarily composed of protein, so ensure you have an adequate intake of protein-rich foods like eggs, lean meats, fish, nuts, and legumes.
Vitamins and Minerals: Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure you get a good supply of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, C, D, E, and biotin.
Hydration:
Water Intake: Stay hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day. Dehydration can affect hair health.
Scalp Care:
Regular Washing: Clean your hair and scalp regularly to remove dirt and excess oil. However, avoid overwashing, as it can strip the hair of natural oils.
Gentle Shampoo: Use a mild, sulfate-free shampoo that suits your hair type and scalp condition.
Scalp Massage: Stimulate blood flow to the scalp by massaging it gently. This can promote hair growth.
Protective Styling:
Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Tight hairstyles, like ponytails or braids, can cause stress on the hair and scalp. Opt for looser styles to prevent breakage.
Protective Styles: Consider protective hairstyles that minimize manipulation and protect the ends of your hair.
Heat Styling and Chemicals:
Limit Heat Styling: Reduce the use of heat styling tools like flat irons and curling irons. If you must use them, apply a heat protectant.
Minimize Chemical Treatments: Limit the use of harsh chemical treatments, such as perms or relaxers, as they can damage the hair structure.
Regular Trims:
Trim Ends: Regular trims help prevent split ends and promote overall hair health. Aim for a trim every 6-8 weeks.
Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure:
Protective Measures: If you spend a lot of time in the sun, protect your hair from UV damage by wearing a hat or using products with UV filters.
Supplements:
Consult a Professional: If needed, consult with a healthcare professional or a nutritionist to determine if you need supplements, such as biotin or omega-3 fatty acids.
Reduce Stress:
Stress Management: High stress levels can contribute to hair loss. Practice stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise.
Adequate Sleep:
Quality Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep each night, as it plays a role in overall health, including hair health.
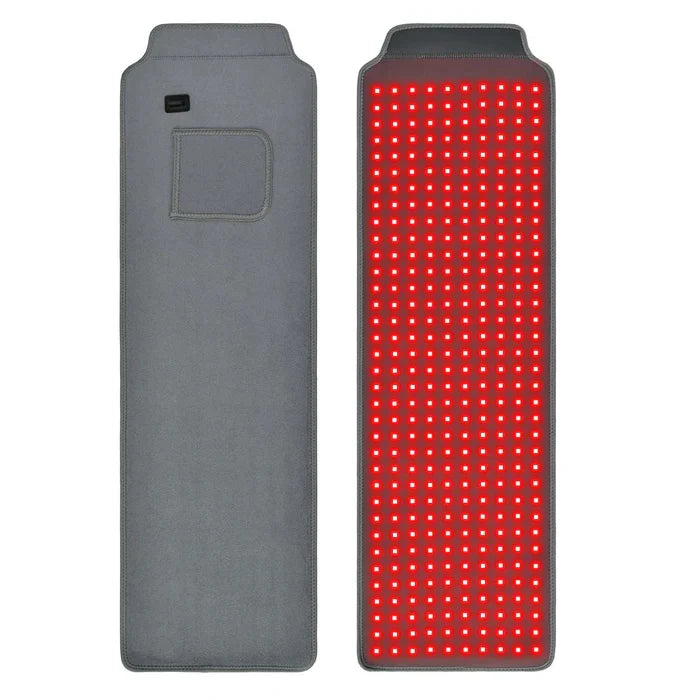
Red Light Therapy:
Red light therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation (PBM), is a form of therapy that uses red or near-infrared light to stimulate cellular function. According to scientific evidence, red light therapy is a safe and effective hair growth treatment. It can fundamentally affect the look and nature of your hair. To try red light therapy for hair development at home, you can browse various devices that suit your requirements and preferences.
Wear a comfortable and stylish red light hair growth cap that will restore your thicker hair in just a few minutes a day. Since it has no known side effects, you can combine it with other treatments recommended by your doctor.

SHOP OUR RED LIGHT THERAPY CAPS
At present, the research progress in hair regeneration has given people with hair loss hope, and the progress in red light treatment is accelerating. When you are facing hair loss problems, try our red light hair growing hat, it will not disappoint you.